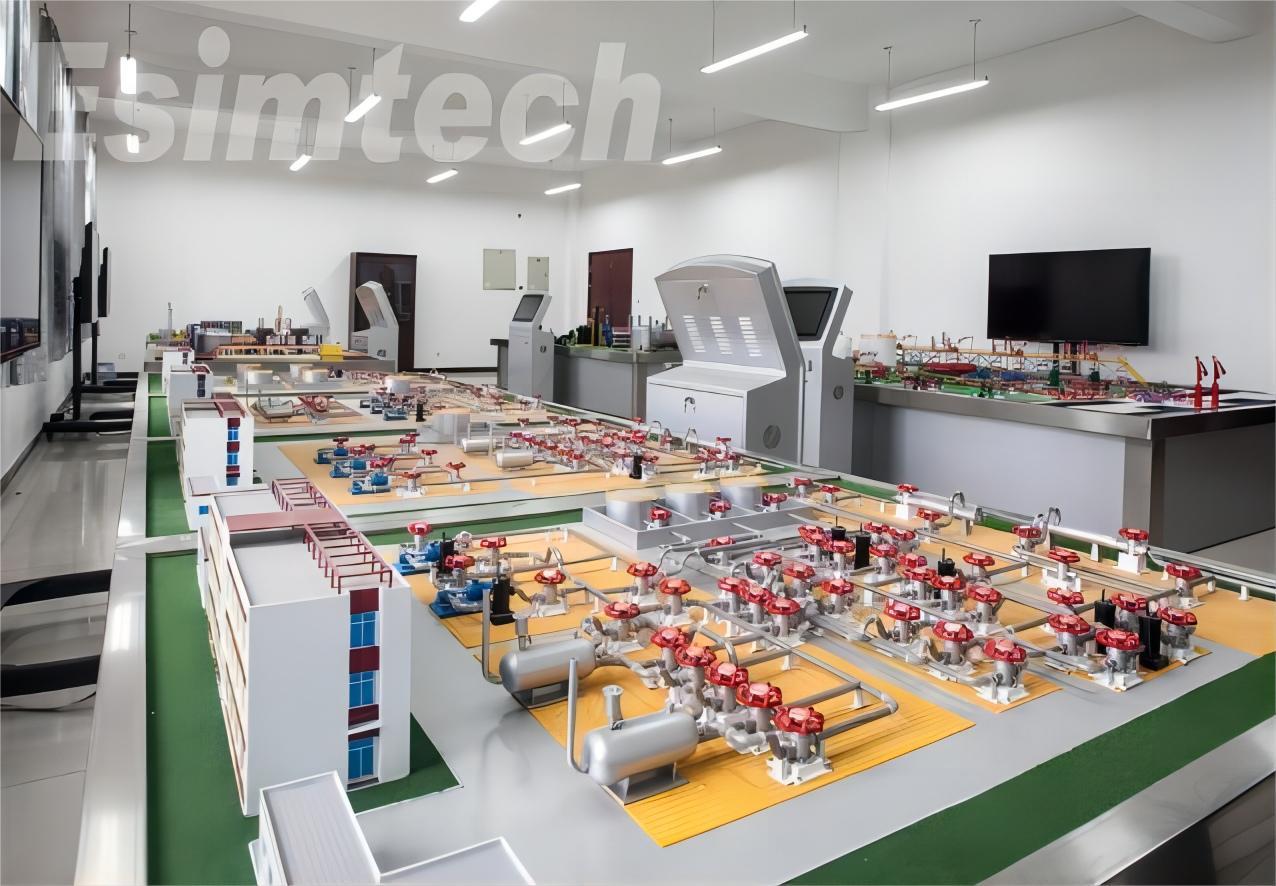
In the intricate web of the oil and gas industry, the efficient gathering and transportation of hydrocarbons from production sites to processing facilities and markets are essential. To ensure the smooth flow of these vital resources, oil and gas gathering, and transportation simulators have emerged as indispensable tools. These simulators play a pivotal role in optimizing logistics, ensuring safety, and minimizing operational risks.
In this article, we will explore the world of oil and gas gathering and transportation simulators, shedding light on their significance, benefits, and applications.
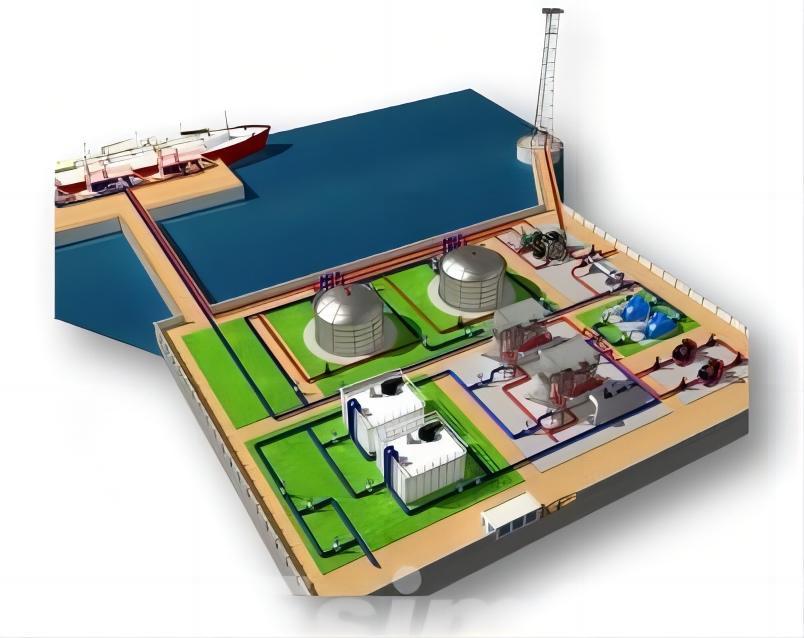
The Complexity of Gathering and Transportation
The gathering and transportation of oil and gas from production sites to processing facilities, distribution points, and ultimately, end-users, is a multifaceted undertaking. The challenges include:
- Network Complexity
Oil and gas infrastructure comprises an extensive network of pipelines, pumping stations, storage tanks, and terminals. Managing this network efficiently requires real-time monitoring and decision-making.
- Fluid Dynamics
Hydrocarbons have diverse properties, and their flow characteristics can change significantly with variations in pressure, temperature, and composition. Predicting these changes is vital for safe and efficient transport.
- Safety and Environmental Concerns
Ensuring the safety of personnel, the environment, and communities along the transportation route is paramount. Any accidents or leaks can have severe consequences.
- Economic Optimization
Maximizing the utilization of existing infrastructure, minimizing energy losses, and reducing transportation costs are essential for the profitability of oil and gas operations.
The Role of Simulators
Oil and gas gathering and transportation simulators are advanced computer-based tools that replicate the complex dynamics of the transportation network. These simulators allow operators and engineers to model various scenarios, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions. Here are some key aspects of their role:
- Optimizing Infrastructure Design
Simulators assist in designing the gathering and transportation infrastructure, helping engineers determine the optimal layout, pipe sizes, and compression facilities.
- Flow Analysis
They provide detailed flow analysis, enabling operators to identify bottlenecks, optimize flow rates, and ensure uniform product delivery.
- Safety Assessment
Simulators allow for safety assessments by modeling potential hazards and identifying measures to mitigate risks, such as leak detection and emergency shutdown systems.
- Maintenance Planning
Predictive maintenance planning is enhanced through simulation, which helps schedule repairs and replacements to minimize downtime.
- Emergency Response Training
Operators and emergency response teams can use simulators to train for various crisis scenarios, ensuring swift and effective responses to incidents.
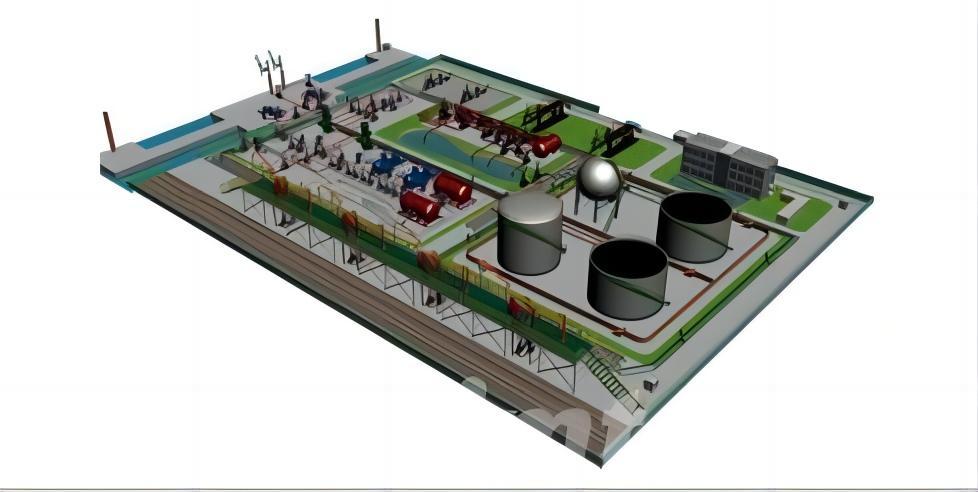
Benefits of Oil and Gas Gathering and Transportation Simulators
The implementation of simulators in oil and gas gathering and transportation systems offers a range of significant benefits:
- Cost Reduction
By optimizing infrastructure and reducing operational inefficiencies, simulators help cut transportation costs and enhance profitability.
- Enhanced Safety
Through the modeling of safety measures and emergency procedures, simulators contribute to improved safety standards and a reduced likelihood of incidents.
- Environmental Impact Mitigation
Simulators can be used to assess and minimize the environmental impact of transportation operations, including emissions modeling and spill response planning.
- Asset Lifecycle Management
Predictive maintenance facilitated by simulators prolongs the lifespan of transportation assets, reducing the need for costly replacements.
- Regulatory Compliance
Simulators assist in meeting regulatory requirements, ensuring that transportation operations adhere to industry standards and government regulations.
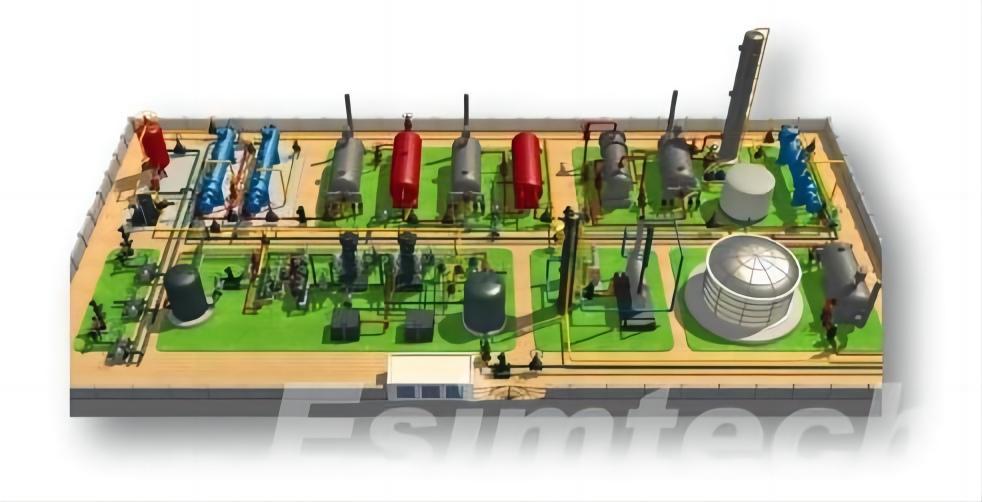
Applications of Oil and Gas Gathering and Transportation Simulators
- Pipeline Simulation: Simulators are used to model the behavior of pipelines under different operating conditions, including pressure, temperature, and flow rates. This helps in optimizing pipeline design and performance.
- Marine Transportation Simulation: For oil and gas transported by sea, simulators replicate vessel operations, cargo handling, and emergency response scenarios. This ensures safe and efficient marine transportation.
- Rail and Truck Simulation: Simulators help train operators responsible for the transportation of hydrocarbons via rail and truck, with a focus on safety and efficiency.
- Storage Facility Modeling: Storage facility simulators allow operators to manage the inventory and storage of hydrocarbons effectively, preventing overflows or shortages.
Conclusion
Oil and gas simulators are vital for a precise, safe, and efficient industry. As global energy demands rise, they ensure smooth hydrocarbon transport, improving infrastructure, safety, and sustainability in the energy supply chain, benefiting economies worldwide.
